Introduction
The most amazing gesture that can be shown by one person to another is the smile. Smile is the feeling of joy that is reflected on a person face, if the person is genuinally happy. A beautiful smile is the combination of three major factors i.e. the competent lips, the shape, size, and alignment of teeth in the arch, and the color of gingiva.1 The normal color of gingiva is coral pink in the British population and pale pink in the Indian population. This color of gingiva relies to a much extent upon the color of the skin, which further relies upon various pigments like melanin, haemoglobin, and keratin.2 Among them melanin has the highest influence on the color of the gingiva. Melanocytes are dendritic cells located in basal and spinous layres of gingival epithelium. They synthesize melanin in organelles called premelanosomes or melanosomes. These contain tyrosinase, which hydroxylates tyrosine to dihydrophenylalanine (DOPA), which in turn progressively converted to melanin. This melanin when secreted in excess, can lead to pigmented gingiva which varies in color from blackish, bluish, to brownish which may have an esthetic concern while smiling. According to Dummett Oral pigmentation index, the incidence of oral pigmentation was gingiva (60%), hard palate (61%), mucous membrane(22%), tongue(15%).3 Hence a procedure called as depigmentation is used to treat this pigmented gingiva. This depigmentation procedure is carried out by various methods such as by scalpel, electrosurgery, cryosurgery, lasersand radiosurgery., by rotary bur as each technique having its own significance, advantages, and disadvantages.4
Case History
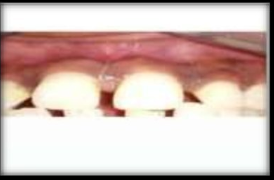
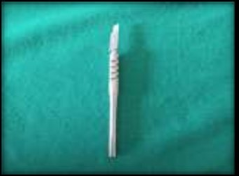
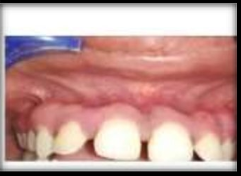
Present case report is on a 21 years old female patient who came to Peoples College of Dental Science and research centre in the department of Periodontology, with the chief complaint of display of blackish gums while smiling. Upon examination, the patient did not have any contributing medical history. There was pigmented gingiva in maxillary tooth region beginning from incisors to Premolars. So after giving local infiltration from maxillary incisors to maxillary premolars, depigmentation by scraping method by scalpel was performed by keeping the surgical scalpel parallel to the long axis of the teeth, and scraping the pigmented gingiva in layers. After two weeks of the surgery, there was restoration of the normal pale pink color of gingiva and the healing was uneventful.
Discussion
Melanin is the pigment that is secreted by the melanocytes, and is responsible for color of the skin, including the soft tissues of the oral cavity, i.e. gingiva. Amount of pigmentation is identified according to Dummett, oral pigmentation index, which shows highest pigmentation in palate, followed by gingiva.3 This pigmentation can vary depending upon individual skin color. The color of this gingival pigmentation can vary from blue, brown, black. Depigmentation is the procedure used to treat the gingival pigmentation. Various techniques are there for gingival depigmentation, each having its own advantages, limitations, and significance. 4 In our case report, gingival depigmentation was carried out by surgical scalpel by scraping method. Tipton et al found that the surgical wound by scalpel heals much faster as compared to the electrocautery induced wound.5 Scalpel surgical technique was first demonstrated by Dummet and Bolden in which they found that scalpel surgical technique is simple, easy to perform, non-invasive, cost effective, doesnot require any special armanterium, and faster healing.6