Introduction
The odontogenic cysts such as dentigerous cyst (DC), odontogenic keratocyst, radicular cysts, calcifying odontogenic cysts, and glandular odontogenic cysts are more potential towards neoplastic transformation, among them odontogenic keratocyst and DC has highest potential.1 DC is the commonest odontogenic cysts more prone to develop from odontogenic tissue encompassing an impacted tooth. Clinically, most commonly associated with an impacted mandibular third molar followed by maxillary canine and mandibular premolars. Radiographically, reveals a well-defined unilocular radiolucency with sclerotic border encircling crown of an impacted tooth.2
Although rare, DC has the highest potential rate to undergo neoplastic or malignant transformation such as adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (AOT),3, 4 complex odontoma (CO),5 ameloblastoma (AB),6 mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC),7 and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)1, 8 have been documented in the literature. But in the literature till now only few cases reported where DC undergoing malignant transformation.9 Here, we present a rare case of carcinoma arising from DC in 50 years old male patient.
Case Report
A 50 years old male patient reported to the department with a chief complaint of pain and swelling on left side, lower one third of the face. He reveals swelling since 3 months and pain since one week. Past medical and dental history non-contributory. On extra oral examination revealed a diffused swelling on left lower one third of the face, measuring approximately 5 x 5.5 cms. The skin over swelling was stretched and shiny. No discharge and no ulcerations were noted. On palpation, it was firm to hard in consistency and tender. No associated lymphadenopathy was found. On intra oral examination, vestibular obliteration with intact surrounding mucosa was noted. On palpation it was firm to hard in consistency and tender. Based on the patient’s history and clinical examination a provisional diagnosis of ameloblastoma was made. [Figure 1 ]
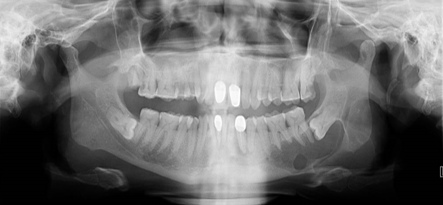
Base line investigations were non-contributory. Radiological investigations such as OPG revealed [Figure 2 ] a well-defied unilocular radiolucency with respected to horizontal impacted left mandibular third molar. Perforation of lingual cortical plate was noted (a well-defined round unilocular radiolucency was noted). Right horizontal impacted mandibular third molar tooth, endodontically treated with fixed prosthesis with respect to 11,21,42, and 33, grossly decayed tooth with respect to 16, decayed tooth with respect to 27 and endodontically treated 33 with periapical radiolucency were noted. Chest x-ray was taken which was non-contributory. Based on the radiological features unicystic ameloblastoma arising from dentigerous cyst was made.
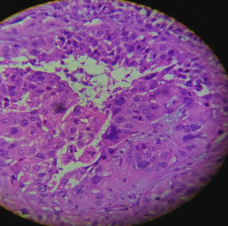
Incisional biopsy was performed, which revealed many sheets and clusters of cells, multiple keratin pearl formations and focal mucinous and cystic change. The cells polygonal in shape and contain moderate to abundant bright acidophilic cytoplasm and sharp cellular margins. The nucleus is round to oval and show moderate pleomorphism, disorganization, coarse chromatin clumping and prominent nucleoli. Mitotic activity is high. There are patchy areas of stromal desmoplastic reaction and dense infiltrates of lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils suggestive of invasive keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. [Figure 3 ] The patient underwent surgical hemimandibulectomy followed by radiation therapy.
Discussion
Squamous cell carcinoma come into existence from odontogenic cysts is extremely rare and till know nearly 100 cases reported in the literature.10 The most common odontogenic cysts under goes malignant transformation are radicular cysts (60%), dentigerous cysts (16%), odontogenic keratocyst (14%) and lateral periodontal cysts (1%) have been also reported.10, 11 The present case reported was a squamous cell carcinoma arise from dentigerous cysts.
Squamous cell carcinoma arise from DC undergoes neoplastic transformation at incidence of 1% to 2.5%9 and malignant transformation at an incidence of 1% to 2%.12 The most common site of occurrence is mandibular third molar followed by maxillary canine. Predominantly seen at age group between 37-90 years with male predominance at a ratio of M:F is 3:1.13 The present case was consistent with the literature.
The exact etiopathogenesis is still unknown, but the chronic inflammation and infectious tissue has been suggested one of the predisposing factor for malignant transformation of the cystic epithelium. 8, 14 Gulbranson et al.15 suggested oncogenes plays important role in transformation of follicular cyst without chronic inflammation to malignancy. According to vander Wal et al.16 and Browne et al.17 keratinisation in the epithelial lining could be a risk factor for malignancy.
Clinically, represented as a diffuse swelling with pain in most of the cases, mobile teeth and cortical expansion as well perforation as reported in our case. Lymphadenopathy and numbness are reported less frequently,18 in the present case lymphadenopthay was noted which are mobile and tender. Radiographically, it is so difficult to diagnose the malignant changes from odontogenic cysts in early stages. The diagnosis is purely based on the patient’s history and clinical examination and it is considered mostly on aggressive growth of lesions at an area occurs. Radiographically, it is represented as a well-defined unilocular radiolucency with or without cortical perforation. The present case reported was consistent with the literature.
Surgical management is the key method, including prophylactic and surgical excision of involved lymph nodes.19 En-bloc surgery is the safest surgical modality to ensure disease-free survival with least recurrence rate of ˂ 15%.20
Conclusion
Among all the odontogenic cysts, dentigerous cyst is one of the more commonly encountered in routine practice. The neoplastic transformation rate is noted in odontogenic cysts. Thus, there is a need of a thorough knowledge and complete evaluation of impacted teeth and its removal should remain as acceptable therapy. The complete histopathological evaluation of excised specimen of dentigerous cyst to rule out its complications.