- Visibility 117 Views
- Downloads 15 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpi.2024.025
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Oral pathogens and respiratory illness: Understanding the link between dental and lung health- A literature review
Introduction
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease affecting the tissues around the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss and the degradation of the surrounding alveolar bone. Various criteria are used globally to diagnose periodontitis, but the WHO's commonly accepted criteria include gingival inflammation, alveolar bone and connective tissue loss, increased probing depths, and the formation of periodontal pockets.[1] Periodontal diseases are caused by bacteria and are associated with inflammation, bacteremia, and a strong immune response. [2] If there is any uncertainty, it is important to consider that the patient may have additional underlying medical conditions that should be evaluated to determine the most appropriate treatment. [1]
Preventive measures
Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss and the deterioration of the alveolar bone. Various diagnostic criteria are used worldwide, with the WHO's widely accepted standards including gingival inflammation, loss of alveolar bone and connective tissue, increased probing depths, and the development of periodontal pockets. Periodontal diseases are bacterial in origin and are linked to inflammation, bacteremia, and a robust immune response. If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, it is important to consider that the patient might have additional underlying medical conditions that need to be assessed to determine the most suitable treatment. [1]
Measuring instrument
A periodontal probe is utilized to measure the distance from the cementoenamel junction to the base of the periodontal pocket, enabling the classification of periodontitis into three grades: mild, moderate, and severe. Periodontitis is recognized as an inflammatory disorder of the gums. Factors contributing to dental caries include poor oral hygiene, substance use, smoking, changes in the immune system, aging, diabetes, and chronic plaque buildup. [1]
Discussion
Respiratory illness associated with periodontitis
Periodontal diseases, caused by bacteria, are associated with inflammation, bacteremia, and a strong immune response. Respiratory disorders cause significant suffering and a high number of fatalities in humans. Specifically, periodontal disease may influence the bacterial pathogens responsible for respiratory illnesses such as pneumonia and COPD. [2]
Pneumonia infects the pulmonary parenchyma and can be caused by various infectious organisms, including viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma, fungi, and parasites. Bacterial pneumonia is likely to become increasingly significant in the coming years due to the continuous development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as penicillin-resistant pneumococci. [2]
Pneumonia classified as 2 types:
Hospital acquired
Community acquired
Periodontal disease can lead to respiratory conditions such as pneumonia and COPD. This illness, characterized by the chronic obstruction of airflow, is primarily caused by chronic bronchitis (CB) and/or emphysema, which result in increased sputum production. [2]
Periodontitis is a major factor in systemic disorders, including respiratory illnesses like COPD. Aspiration of contaminated oral secretions can inflame the airway mucosa, leading to respiratory diseases. Salivary enzymes and cytokines from periodontal infections, such as IL-6, have been shown to accelerate the development of respiratory infections. While periodontal infections may not directly cause systemic lung involvement, it is evident that these two conditions share common risk factors, including potentially shared pathogenic organisms involved in both disorders. [1]
In high-risk patients with poor oral hygiene, dental plaque and pockets can serve as reservoirs for respiratory infections. Bacteria such as Streptococcus and Hemophilus, which are associated with periodontal diseases, can exacerbate lung infections in COPD patients. Oral health is a significant risk factor for systemic disorders; tooth decay, the presence of cariogenic bacteria, and periodontal infections have been shown to considerably increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia. However, maintaining good dental hygiene can reduce the impact of pneumonia. [3] Periodontal disease and poor oral hygiene are also linked to other respiratory conditions, including COPD, which affects up to 15 million people and is the fourth leading cause of death in the US. The infection processes may involve oral pathogens causing pneumonia by aspiration into the lungs, respiratory pathogens colonizing dental plaque and then being aspirated, or periodontal pathogens facilitating the colonization of pulmonary pathogens in the upper airway. [2]
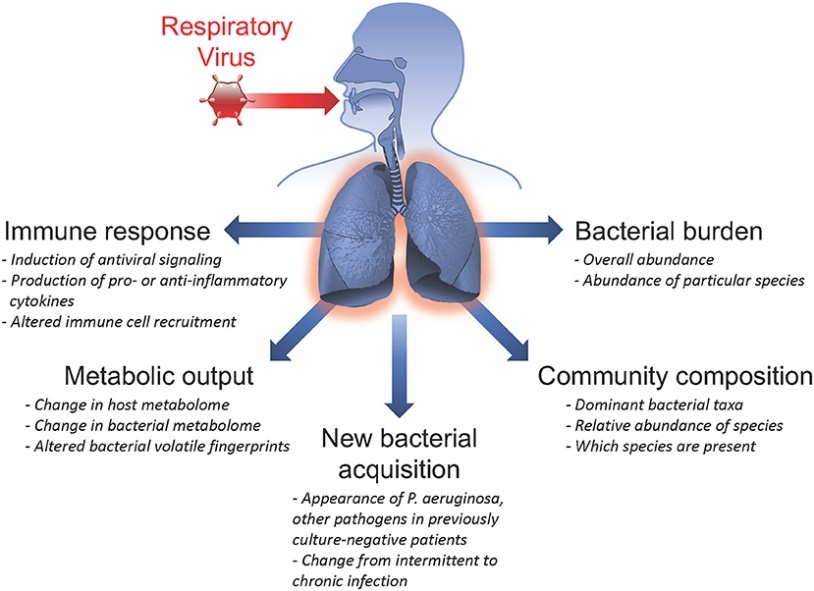
Proinflammatory cytokines are crucial in lung inflammation during pneumonia and COPD exacerbations. Research has shown that killed periodontopathic bacteria, such as P. gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum, induce substantial secretion of proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-8 from human epithelial cell lines derived from the bronchi, alveoli, and pharynx. This effect was also observed in primary human respiratory epithelial cells. Furthermore, intratracheal inoculation of these periodontal pathogens in mice significantly increased the secretion of IL-6 and KC (the mouse equivalent of IL-8) in the lungs and bronchi. Remarkably, high levels of these cytokines were also detected in the blood of the mice, with concentrations several times greater than those produced by S. pneumoniae.
The development of the bacterial infection in oral due to bacteria by the oral bacterial species implicated in causing pneumonia and lung abscesses include Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Actinomyces israelii, Capnocytophaga species, Eikenella corrodens, Prevotella intermedia, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and Streptococcus constellatus.
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the potential role of oral bacteria in the development of respiratory infections: [4]
Inhalation of Oral Pathogens: Oral infections, such as those caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, can be inhaled and lead to lung infections. [5]
Salivary Enzymes: Enzymes associated with periodontal disease may modify mucosal surfaces, promoting the adherence and colonization of respiratory pathogens, which are then inhaled into the lungs.[6]
Recent studies have highlighted a link between respiratory infections and poor oral health. At least six recent investigations have established this connection, with two cross-sectional epidemiological studies specifically suggesting an association between COPD and poor oral health. The available evidence indicates that dental health problems can be a significant risk factor for lower respiratory infections, especially in high-risk populations. [2]
A significant correlation was observed between the prevalence of nosocomial pneumonia and bacteremia and the colonization of dental plaque on days 0 and 5. When a nosocomial infection occurs, the pathogen is initially identified in the dental plaque. Consequently, elevated levels of salivary hydrolytic enzymes due to poor oral hygiene may lead to an increased dental plaque load. This, in turn, could result in the breakdown of protective elements of host secretory components (such as mucins), thereby diminishing non-specific host defenses against respiratory pathogens in high-risk individuals. [7]
Over the past few decades, the link between periodontitis and various respiratory diseases has been extensively studied. Several systematic reviews have suggested a connection between poor oral health and respiratory conditions. Although numerous studies indicate that improved dental hygiene can help prevent several respiratory illnesses, this topic remains under investigation. Increasing research has highlighted a correlation between periodontal disease and asthma, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting individuals of all ages. [6] Reduced salivation and lower salivary pH, which are common in sick individuals and those taking various medications, can facilitate the colonization of respiratory pathogens. Oral colonization by respiratory infections is notably prevalent among hospitalized patients, especially those in intensive care units, elderly patients in hospitals, nursing home residents, and those with severe disabilities. [8]
The four modes of infection dissemination include hematogenous spread from extrapulmonary infection sites, such as translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. [4]
Pathogenesis
As previously noted, periodontitis is an inflammatory disorder affecting the gums. Contributing factors include poor dental hygiene, smoking, drug use, prolonged plaque accumulation leading to dental caries, weakened immune systems, aging, and diabetes. The primary inflammatory response in periodontitis is driven by neutrophils. An excessive neutrophil response in the periodontal tissues leads to inflammation characterized by swelling, congestion, bleeding, and eventually detachment of the periodontium from the teeth, which results in tooth loss. This condition arises from a combination of factors, including bacterial growth, food particle accumulation, inadequate hygiene practices, genetic predispositions, and occasionally immunosuppressive conditions. Thus, periodontitis results from a complex interplay of intrinsic, environmental, and genetic factors. [1]
In addition to a neutrophil-induced response, the respiratory pathology of COPD is associated with several risk factors, including the accumulation of pulmonary pathogens in the airways, a weak cough reflex, smoking, aspiration of irritating substances, and poor dental hygiene. Normally, the lower airways are sterile. This sterility is maintained by the mucociliary layer, which propels inhaled bacteria and irritant particles toward the oropharynx, as well as by immune and non-immune defense mechanisms. [9] These defenses include the surfactant layer, which contains fibronectin, complement proteins, immunoglobulins, and phagocytic cells to remove particulate debris and help preserve the sterility of the lower airway.
Oral infections can lead to immediate lung infections. Research has linked periodontal organisms such as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis to aspiration pneumonia. [10] Additionally, it is important to recognize that pulmonary pathogens can colonize dental biofilm, supporting the idea that the oral cavity may act as a reservoir for bacteria responsible for aspiration pneumonia in high-risk individuals.
Salivary enzymes associated with periodontal disease can alter the mucosal surfaces of the respiratory tract. According to this theory, these enzymes facilitate bacterial adherence and colonization, leading to pathogen aspiration into the lungs and subsequent infection. Potential mechanisms by which mucosal surfaces are altered to increase adhesion include: [11]
High concentrations of proteolytic periodontal bacteria and their specific enzymes, such as mannosidase, fucosidase, hexosaminidase, and sialidase, which modify the mucosal epithelium.
Exposure of surface receptors due to the loss of surface fibronectin, a protein that normally covers the mucosa.
Elimination of surface fibronectin by hydrolytic enzymes.
Release of cytokines.
Despite the wide range of hydrolytic enzymes in saliva, salivary enzymatic activity is closely related to an individual’s dental hygiene and periodontal health.[11]
Periodontopathic bacteria's hydrolytic enzymes can disrupt the salivary film's defense against pathogenic bacteria
Periodontopathic bacteria's hydrolytic enzymes can compromise the salivary film’s defense against pathogenic bacteria. These enzymes may reduce the ability of mucins to bind to viruses like Haemophilus influenzae, allowing the viruses to adhere more readily to mucosal receptors in the respiratory system. For example, P. gingivalis produces enzymes that degrade salivary molecules and disrupt the protective salivary film on mucosal surfaces, exposing respiratory pathogens to adhesion receptors. Individuals with poor dental hygiene may have elevated levels of these hydrolytic enzymes in their saliva.
When periodontal disease is left untreated, especially in high-risk individuals, a wide range of cytokines and other biologically active substances are continuously released from periodontal tissues and peripheral mononuclear cells. These substances can alter the respiratory epithelium, upregulate adhesion receptors on mucosal surfaces, and facilitate the colonization of respiratory pathogens, leading to infection. [12]
Seasonal influenza, caused by influenza A and B viruses, often leads to severe illness and death, particularly in individuals with underlying health conditions and the elderly. Influenza A and B viruses have hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) spikes on their surfaces, which are crucial for the adsorption and release of the virus during replication. During adsorption, HA binds to sialic acid on the host's upper respiratory mucosa, allowing the virus to attach to and enter the target cell. Inside the cell, viral nucleic acids and proteins are synthesized and assembled into new viral particles, which initially remain attached to the cell surface due to sialic acids.[13] The release of these progeny viruses does not occur until NA degrades the sialic acid, which allows the progeny viruses to detach from the infected cell and spread to neighbouring cells.
Excessive mucin production in patients with pneumonia and COPD not only leads to increased sputum production but also causes bronchial lumen obstruction, thereby impairing respiratory function. Research using primary human bronchial epithelial cells demonstrated that Porphyromonas gingivalis [14] strongly induces the expression of MUC5AC, a key mucin protein. The gingipains produced by P. gingivalis were found to be central to this effect. Additionally, P. gingivalis significantly increased MUC5AC expression and mucin production in murine lungs, while strains deficient in gingipains did not produce this effect. It is suggested that gingipains from P. gingivalis may impair respiratory function by inducing excessive mucin production in the lungs and bronchi, leading to bronchial lumen narrowing.
Moreover, periodontopathic bacteria have been shown to disrupt the barrier function of both the bronchial and alveolar epithelium in experiments with cultured cell systems and COPD model mice. In mice with intratracheal inoculation of periodontopathic bacteria, there was a significant increase in the mean interalveolar distance, indicating destruction of the alveolar walls. MMP-12 expression, which is associated with alveolar wall destruction, was elevated, while the expression of claudin-1 and JAM-A, which are critical for epithelial barrier formation, was significantly reduced. Additionally, research by Benedyk et al. reported that gingipains from P. gingivalis can destroy mouse alveoli. [15]
Infections can reach the lungs through three main routes: hematogenous spread, airway contamination, and transmission from nearby infection sites, such as the oral cavity. Oral flora species linked to lung infections include Actinomyces israelii, Eikenella corrodens, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Prevotella intermedia, and Streptococcus constellatus.[16] These microorganisms can adhere to mucosal surfaces, be aspirated with oral secretions, resist salivary enzymes that break down tissue, and alter cytokine profiles that affect the respiratory epithelium, contributing to their pathogenic potential.
Conclusion
Periodontitis can lead to the aspiration of oral secretions into the lungs and influence the progression of pulmonary diseases. It is also a major source of lung infections. In addition to enzymes in saliva, various cytokines, such as IL-6, released from periodontal-infected tissues contribute to the development of respiratory infections. Maintaining good dental health and hygiene may reduce the colonization of harmful pulmonary bacteria in the oropharynx, potentially lowering the overall risk of respiratory infections.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- SA Moghadam, M Shirzaiy, S Risbaf. The Associations between Periodontitis and Respiratory Disease. J Nepal Health Res Coun 2017. [Google Scholar]
- M Bansal, M Khatri, V Taneja. Potential role of periodontal infection in respiratory diseases - a review. J Med Life 2013. [Google Scholar]
- A Azarpazhooh, JL Leake. Systematic review of the association between respiratory diseases and oral health. J Periodontol 2006. [Google Scholar]
- FA Scannapieco, JM Mylotte. Relationships between periodontal disease and bacterial pneumonia. J Periodontol 1996. [Google Scholar]
- F Destefano, RF Anda, HS Kahn, F Williamson, CM Russell. Dental disease and risk of coronary heart disease and mortality. BMJ 1993. [Google Scholar]
- IS Gomes-Filho, SSD Cruz, SC Trindade, JS Passos-Soares, PC Carvalho-Filho, ACMG Figueiredo. Periodontitis and respiratory diseases: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oral Dis 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FA Scannapieco. Role of oral bacteria in respiratory infection. J Periodontol 1999. [Google Scholar]
- FA Scannapieco, RB Bush, S Paju. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for nosocomial bacterial pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A systemic review. Ann Periodontol 2003. [Google Scholar]
- JG Bartlett, SM Finegold. Anaerobic infections of the lung and pleural space. Am Rev Respir Dis 1974. [Google Scholar]
- F Fourrier, B Duvivier, H Boutigny, M Roussel-Delvallez, C Chopin. Colonization of dental plaque: a source of nosocomial infections in intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med 1998. [Google Scholar]
- M Nakamura, J Slots. Salivary enzymes. Origin and relationship to periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res 1983. [Google Scholar]
- IS Gomes-Filho, JS Passos. Seixas da Cruz S. Respiratory disease and the role of oral bacteria. J Oral Microbiol 2010. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- K Imai, T Iinuma, S Sato. Relationship between the oral cavity and respiratory diseases: Aspiration of oral bacteria possibly contributes to the progression of lower airway inflammation. Jpn Dent Sci Rev 2021. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A Hasegawa, T Sato, Y Hoshikawa, N Ishida, N Tanda, Y Kawamura. Detection and identification of oral anaerobes in intraoperative bronchial fluids of patients with pulmonary carcinoma. Microbiol Immunol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- N Ishida, T Sato, Y Hoshikawa, N Tanda, K Sasaki, T Kondo. Microbiota profiling of bronchial fluids of elderly patients with pulmonary carcinoma. J Oral Biosci 2015. [Google Scholar]
- FA Scannapieco, AW Ho. Potential associations between chronic respiratory disease and periodontal disease: analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. J Periodontol 2001. [Google Scholar]
